How to: deploy a Django application using Heroku
Paso 1: First, you need to run the command as shown below.
pip freeze > requirements.txt'Nugget freezing’ The command is used to display all installed files. Equally, ‘pip freeze> requirements.txt’ copies the name of all files to a text file which is named as ‘requirements.txt’.
Later, you can run the command like ‘cat requirements.txt’ to see the contents that are present in the ‘requirements.txt’ proceedings.
cat requirements.txt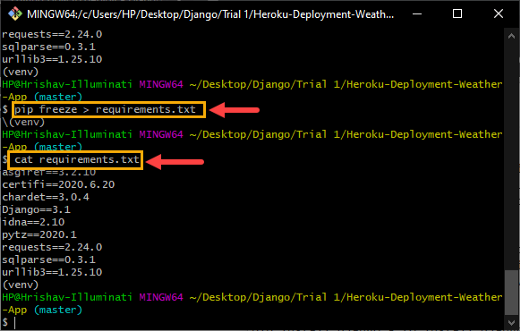
Execution of the ‘pip freeze commands> requirements.txt’ y ‘cat requirements.txt’ in the shell.
Paso 2: Now, go to your Django project and open ‘settings.py’ as shown in the picture below.
Abriendo ‘setting.py’ from the Django project.
Paso 3: Al final de ‘settings.py’ add the following statement.
STATIC_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, ‘static’)Django cannot automatically create a destination directory, namely STATIC_ROOT. Therefore, in ‘settings.py’, a variable called ‘STATIC_ROOT ‘ is responsible for defining the single folder where you are willing to collect all your static files.
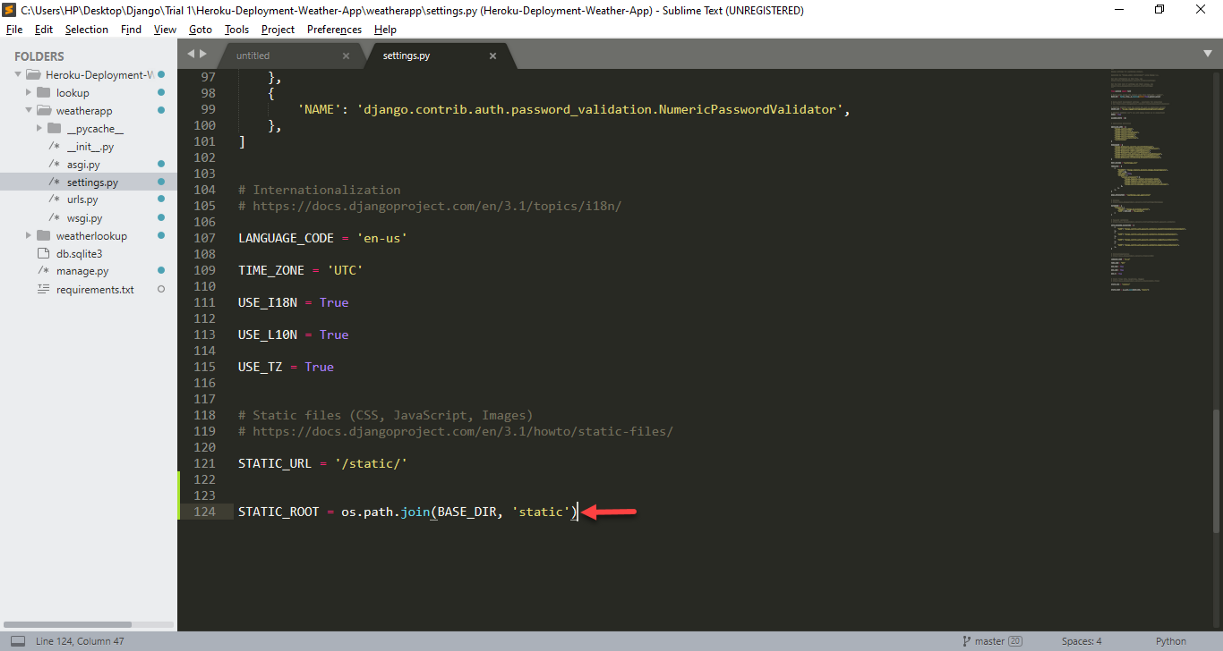
Añadiendo ‘STATIC_ROOT = os.path.join (BASE_DIR,’ static ‘)’ and ‘settings.py’
Note: Before performing the following steps, make sure you have installed Heroku CLI on your PC and have developed a Heroku account. To make sure Heroku has been installed correctly on the PC, run the below command and make sure you get the result as shown in the image below.
heroku -h
Running the command as heroku -h to make sure Heroku is working on PC.
Paso 4: A Procfile is essential in the Heroku application. Therefore, a 'nano command is required’ to edit / create the ProcFile. Therefore, first, you should run the following command.
nano ProcFile
‘Nano ProcFile is running’ to create and edit the file.
Once the files are open, provide the following declaration in the file.
web: gunicorn myproject.wsgiHere, the created ProcFile requires a Gunicorn since it is one of the most preferred production web server for Django applications.
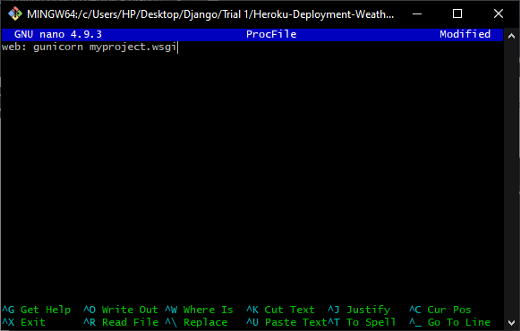
Providing a declaration like 'web: gunicorn myproject.wsgi’ in ProcFile.
After you have provided the statement, press ‘Ctrl + X’ soon 'Pay in’ to save the changes made to the ProcFile.

Presione ‘Ctrl + X’ and then 'Enter’ to save the declaration in the ProcFile.
Paso 5: Now, after you have successfully created the ProcFile, open the given file in text editor. Later, must update 'web: gunicorn myproject.wsgi’ to 'web: gunicorn weatherapp.wsgi’. Updated statement to be updated in ProcFile is provided below.
web: gunicorn weatherapp.wsgiHere, myproject.wsgi updates as weatherapp.wsgi using a text editor (sublime text) as shown in the picture below.
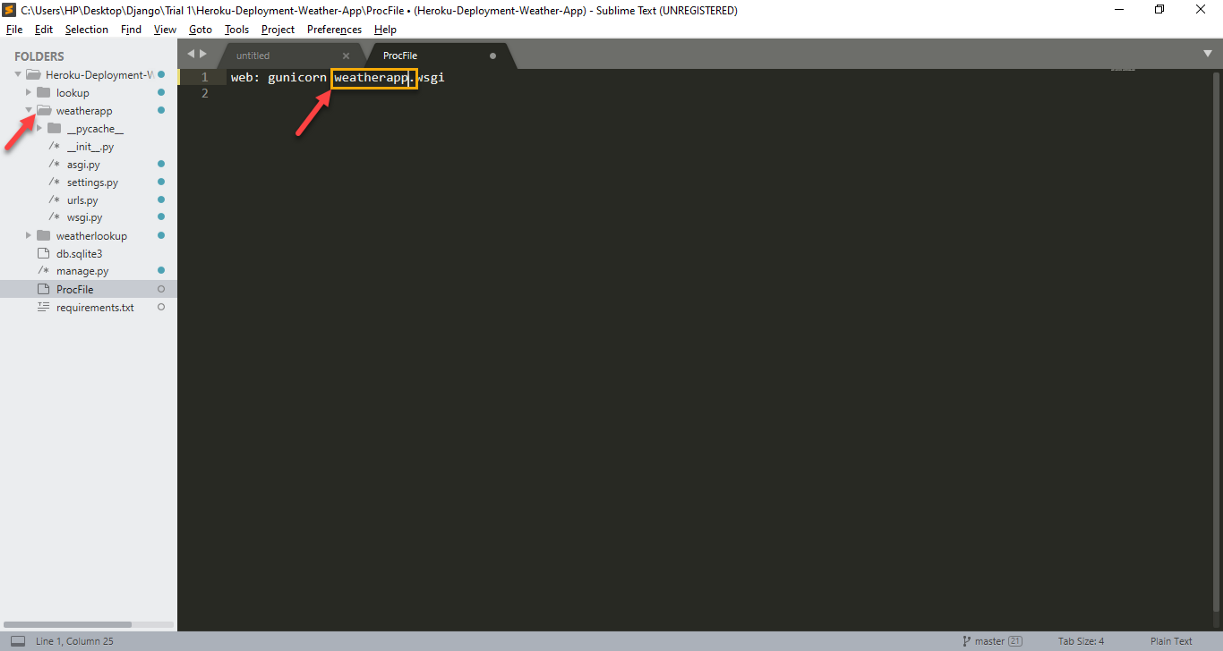
Version upgrade as per requirement
Note: For more information on the Web Server Gateway Interface (WSGI) in detail, visit the link provided below.
Paso 6: Now, you must install Gunicorn.
Therefore, at first, you must run the following queries before doing any more tasks.
pip install gunicorn‘pip instalar gunicorn’ used to install Gunicorn for your project. Finally, now you can run the following commands.
pip freeze > requirements.txtcat requirements.txt
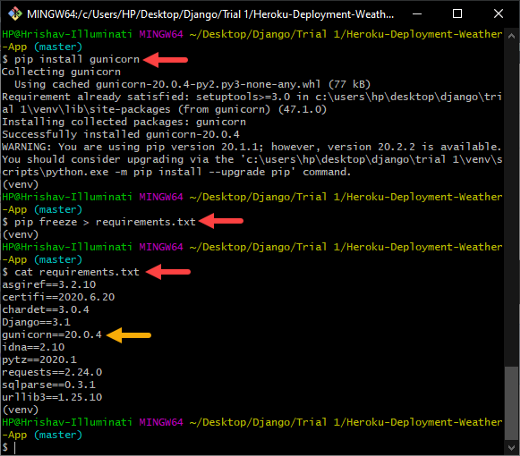
Installing Gunicorn’ and updating the requirements.txt file.
Paso 7: Here, you must install the 'django-heroku' package. Then, to install the package, you should run the following command.
pip install django-herokuThe Django app needs to be configured to work on Heroku. Therefore, ‘django-heroku’ package is able to perform the configurations part automatically which allows your Django application to work with Heroku.
Later, you can run the following commands.
pip freeze > requirements.txtcat requirements.txt
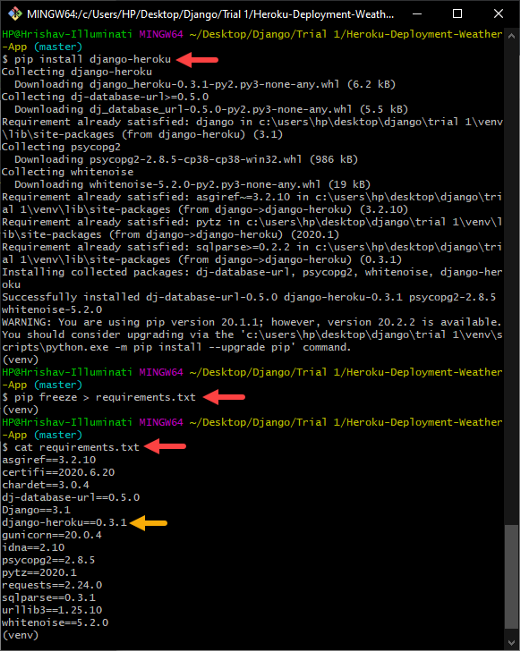
Installing the ‘django-heroku package’ and updating the file ‘requirements.txt’.
Paso 8: Now, you must import the package ‘os’ y ‘django-heroku’ in setting.py as shown in the image below. The code to import the packages is also provided below.
import os
import django_heroku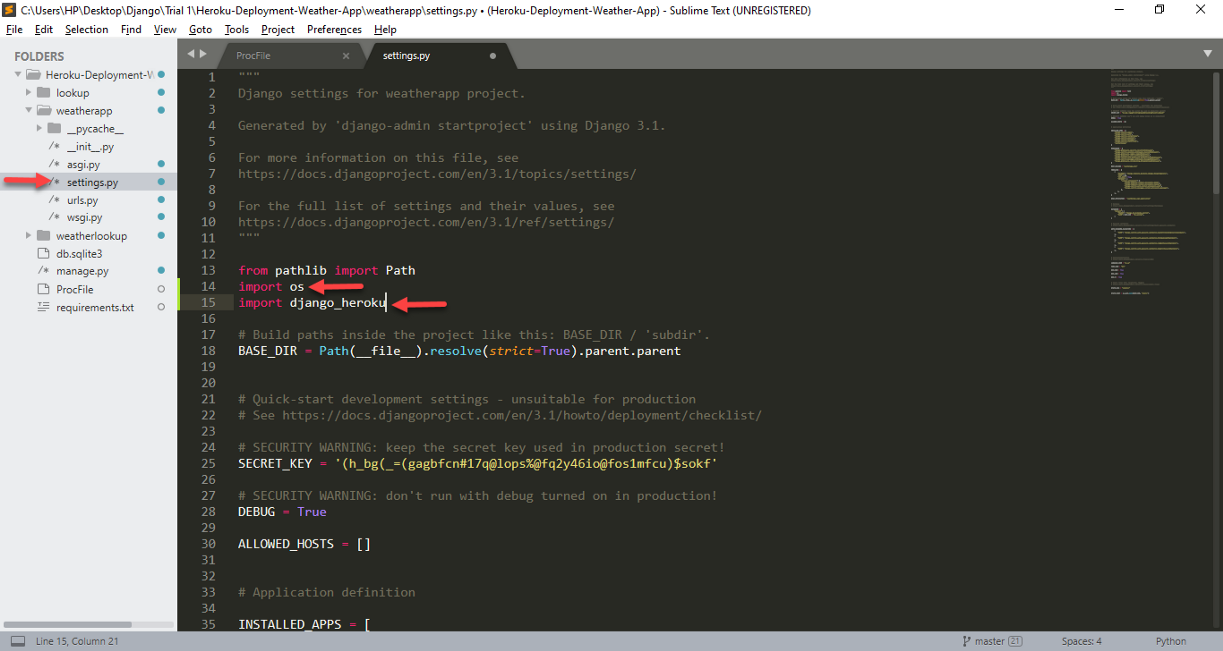
Importing the ‘os package’ y ‘django-heroku’ in setting.py
Paso 9: Now, to activate 'django_heroku’ it should go to the end of ‘settings.py’ and add the following lines of code.
# Activate Django-Heroku.
django_heroku.settings(locals())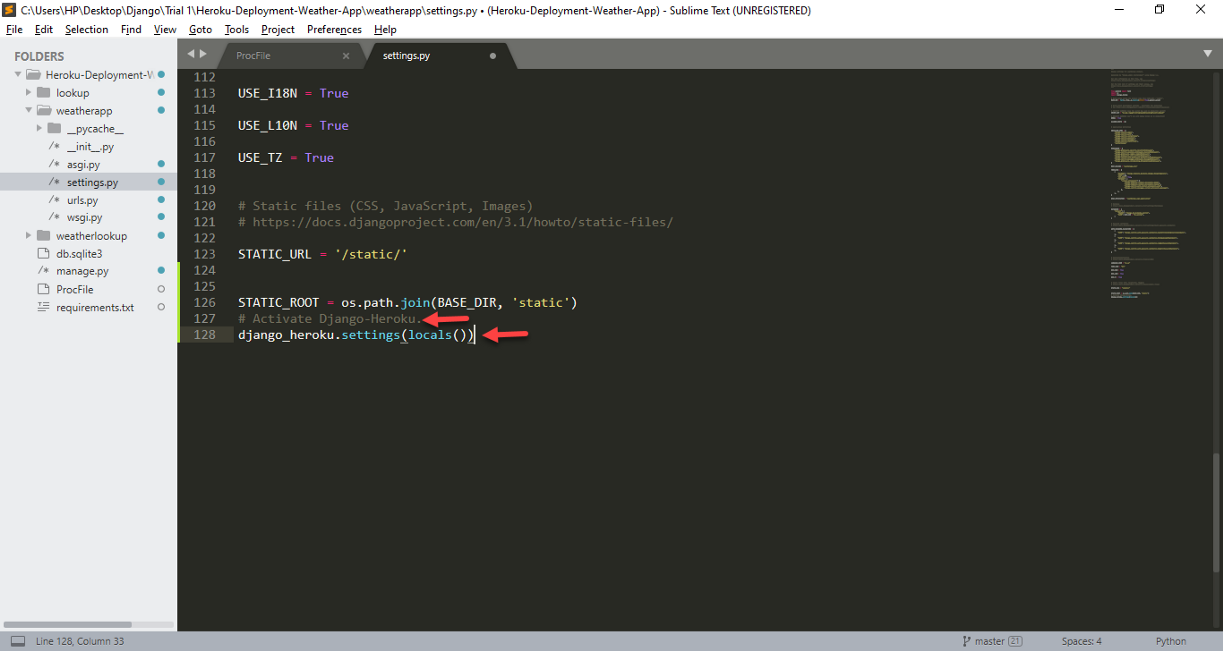
Activating 'django_heroku’ in the Django project
Note: Here, in this blog, we are not using our GitHub repository with the application that will be deployed to Heroku. Therefore, if you have cloned your application from your remote repository, move your app to a new new folder as shown in the image below.
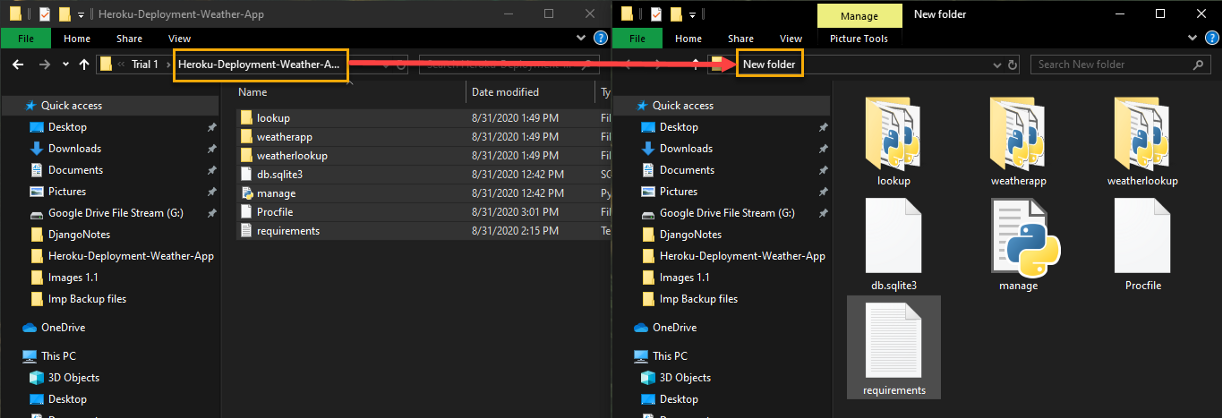
Move the Django application to a new folder.
Paso 10: Since you are now moving to the production site, el ‘DEBUG’ and ‘settings.py’ should be set to 'FALSE’ as shown in the picture below.
DEBUG = FalseLet's get an understanding of – Why do we need to establish DEBUG What Fake?
First, let's understand what happens when DEBUG is set as Certain. DEBUG = True save details about the error pages. Therefore, Django provides a stacktrace of what had gone wrong, which can be very useful when depuration your request. What's more, Django also keeps track of all SQL queries that had been executed in Debugging mode.
Now, let's move on to the result when DEBUG is set as Fake. Keeping the DEBUG way how Certain keeps track of all SQL queries which has been run in DEBUG mode which is Not convenient in the production site. Therefore, now you must provide ALLOWED_HOSTS in the settings.py file that identifies where it is located lodging your django app.
Note: If you need guidance to configure ALLOWED_HOSTS, can go to step 23 of this blog. What's more, I should have created an application on Heroku which was carried out in step 18 before configuring ALLOWED_HOSTS.
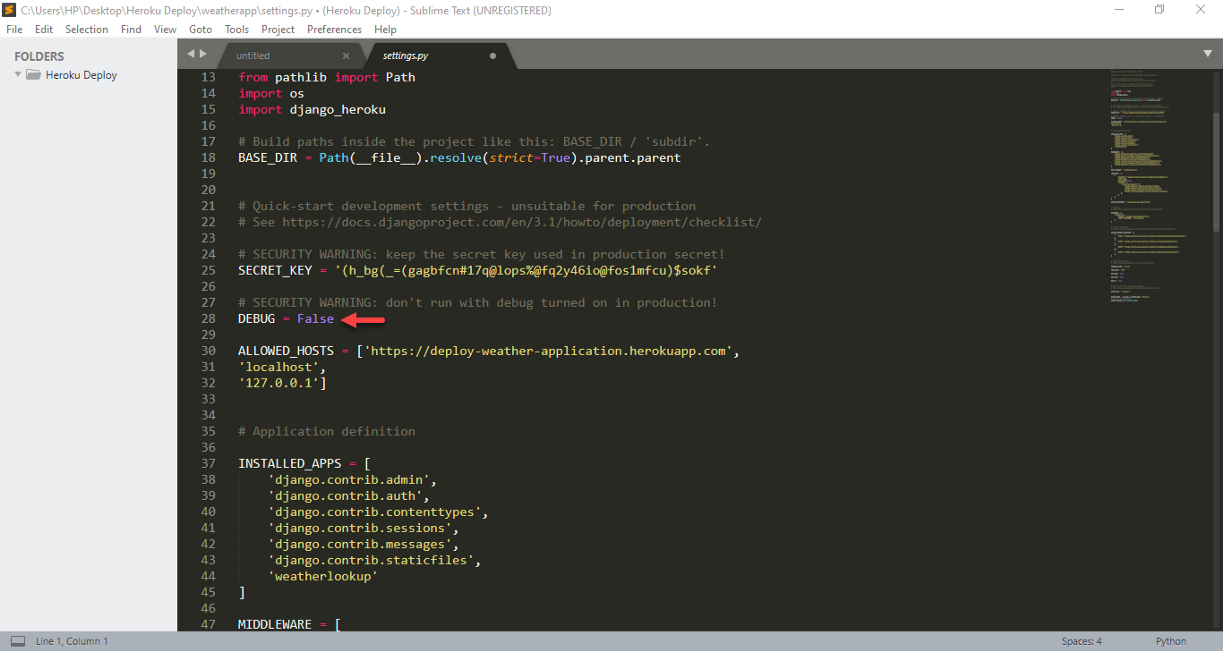
Set 'DEBUG = True’ en ‘DEBUG = False’.
Paso 11: Now, go to your file explorer and right click, then select the option 'Git Bash Here’ as shown in the picture below.
Note: If you haven't installed Git Bash yet and need guidance on installing Git bash, you can see my previous blog, which consists of a detailed procedure to install Git.
Opening the Git Bash terminal.






