Overview
- Skewness is a key statistical concept that you should know in the fields of data science and analytics..
- Learn what skewness is and why it matters to you as a data science professional
Introduction
The concept of asymmetry is embedded in our way of thinking. When we look at a visualization, our mind intuitively discerns the pattern on that graph.
As you already know, India has more than 50% of its population less than 25 years and more than 65% less than 35 years. If you plot the age distribution of the population of India, you will find that there is a hump on the left side of timing and the right side is comparatively flat. In other words, we can say that there is a bias towards the end, truth?
Then, even if you haven't read about skewness as a data science or analytics professional, you have definitely interacted with the concept on an informal note. And it's actually quite an easy topic in statistics and, but nevertheless, many people read it in their rush to learn other seemingly complex data science concepts. For me, That is an error.
Skewness is a fundamental statistical concept that everyone in data science and analytics should know about.. It's something we just can't run from. And I am sure you will understand by the end of this article..
Here, we will discuss the concept of asymmetry in the easiest way possible. You will learn about asymmetry, their types and their importance in the field of data science. So buckle up because you'll learn a concept that you will value throughout your career in data science..
Note: Here are a couple of resources to help you delve deeper into the world of statistics for data science.:
Table of Contents
- What is asymmetry?
- Why is asymmetry important?
- What is a normal distribution?
- Understanding the positively skewed distribution
- Understanding the negatively skewed distribution
What is asymmetry?
Skewness is the measure of the skewness of an ideally symmetric probability distribution and is given by third standardized moment. If that sounds too complex, do not worry! Let me break it down for you.
In simple words, skewness is the measure of how much the probability distribution of a random variable deviates from the normal distribution. Now, I might be thinking: Why am I talking about normal distribution here?
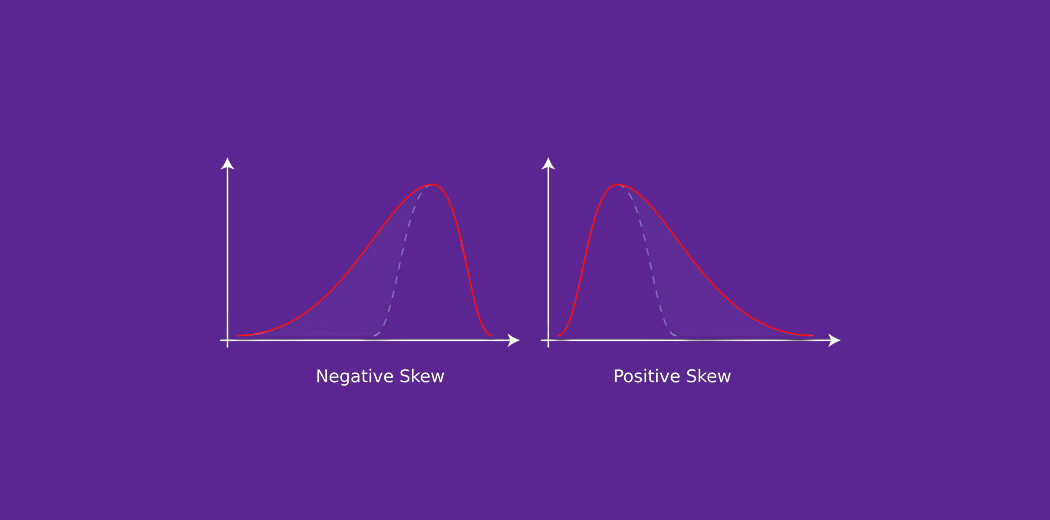
Good, the normal distribution is the probability distribution without any bias. You can see the image below that shows a symmetric distribution which is basically a normal distribution and you can see that it is symmetric on both sides of the dashed line. Apart of this, there are two types of asymmetry:
- Positive bias
- Negative skew
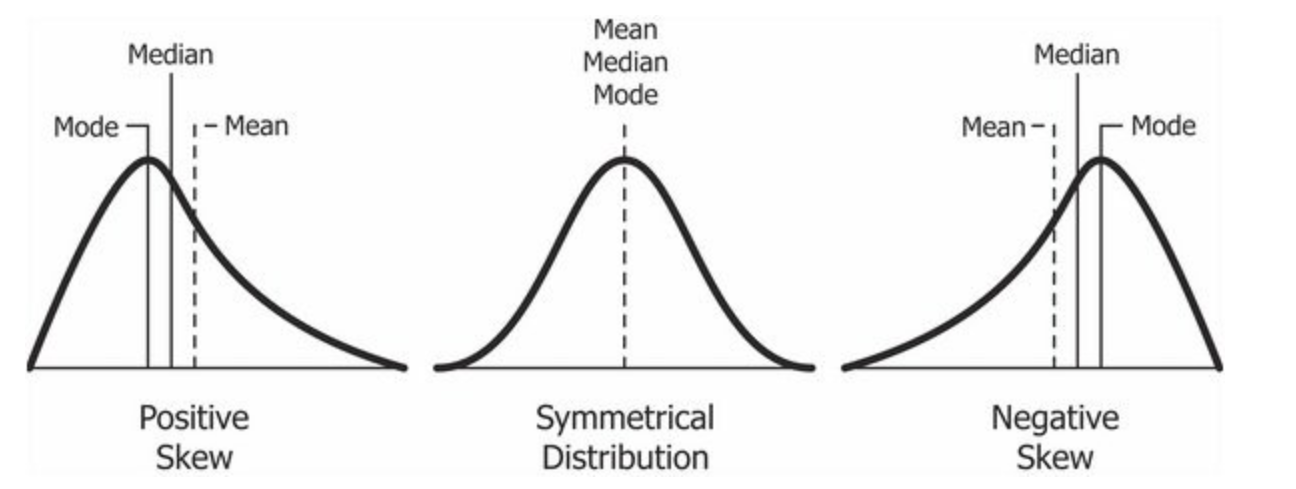
Credits: Wikipedia
The probability distribution with its tail on the right side is a positively skewed distribution and the one with its tail on the left side is a negatively skewed distribution.. If you find the above figures confusing, it's okay. We will understand this in more detail later..
Before that, Let's understand why skew is such an important concept to you as a data science professional.
Why is asymmetry important?
Now, we know that skewness is the measure of skewness and its types are distinguished by the side on which the tail of the probability distribution is located. But, Why is it important to know the skewness of the data?
First, linear models work under the assumption that the distribution of the independent variable and the target variable are similar. Therefore, knowing the skewness of the data helps us create better linear models.
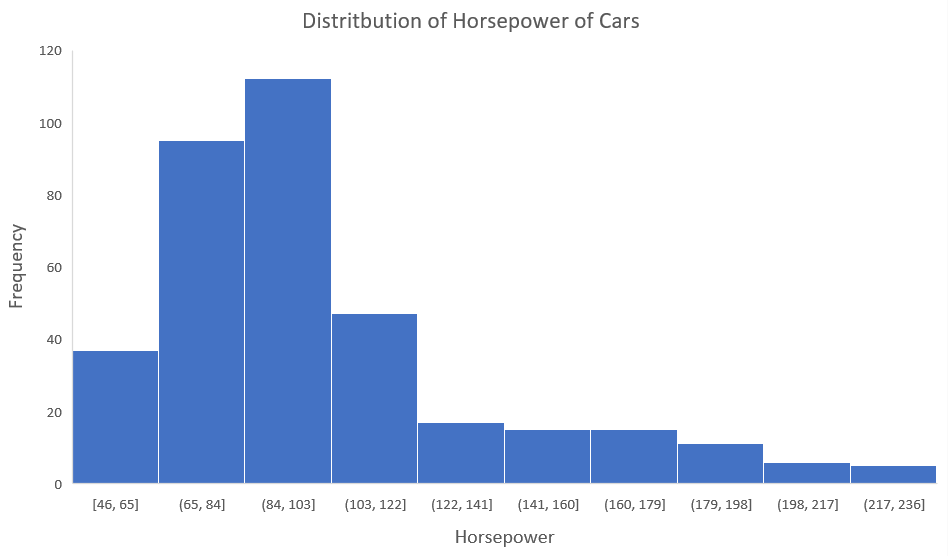
Secondly, let's take a look at the following layout. It is the horsepower distribution of automobiles:
You can clearly see that the above distribution is positively skewed. Now, let's say you want to use this as a function for the model that will predict miles per gallon (miles per gallon) of a car.
Since our data is positively biased here, means you have a greater number of data points with low values, namely, cars with less horsepower. Then, when we train our model with this data, will perform better at predicting the miles per gallon of cars with lower horsepower compared to those with higher horsepower.
What's more, asymmetry tells us about the direction of Atypical values. You can see that our distribution is positively skewed and most of the outliers are present on the right hand side of the distribution.
Note: Skewness does not tell us about the number of outliers. It only tells us the address.
Now that we know why skewness is important, let's understand the distributions that I showed you earlier.
What is symmetric distribution / normal?
Credits: Wikipedia
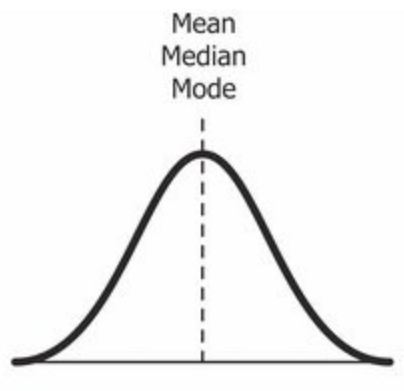
Yes, we return again with the normal distribution. It is used as a reference to determine the skewness of a distribution. As I mentioned before, the ideal normal distribution is the probability distribution with almost no skewness. It is almost perfectly symmetrical. Because of this, the skewness value for a normal distribution is zero.
But, Why is it almost perfectly symmetrical and not absolutely symmetrical?
That is because, in reality, no actual word data has a perfectly normal distribution. Therefore, even the asymmetry value is not exactly zero; it's almost zero. Although the value of zero is used as a reference to determine the skewness of a distribution.
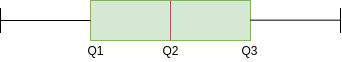
You can see in the image above that the same line represents the mean, median and mode. It is because the average, the median and mode of a perfectly normal distribution are equal.
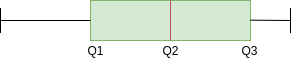
Up to now, we have understood the skewness of the normal distribution using a probability or frequency distribution. Now, let's understand this in terms of a box plot because that's the most common way of looking at a distribution in data science space.
The image above is a symmetric distribution box plot. You will notice here that the distance between Q1 and Q2 and Q2 and Q3 is equal, namely:
But that is not enough to conclude whether a distribution is skewed or not.. We also take a look at the length of the mustache; if they are the same, then we can say that the distribution is symmetric, namely, is not biased.
Now that we have discussed the skewness in the normal distribution, it's time to learn about the two types of asymmetry we discussed earlier. Let's start with the positive skewness.
Understanding the positively skewed distribution
Source: Wikipedia
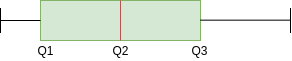
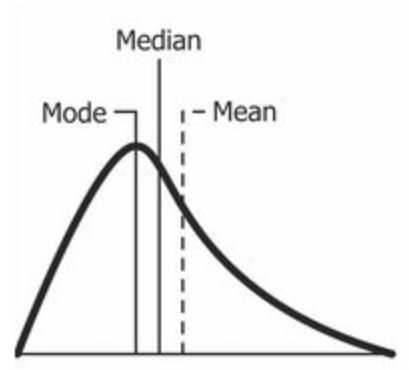
A positively skewed distribution is the distribution with the tail on its right side.. The skewness value for a positively skewed distribution is greater than zero. As you will have understood by looking at the figure, the mean value is the largest, followed by the median and then the mode.
Then, why is this happening?
Good, the answer to that is that the skewness of the distribution is to the right; makes the mean greater than the median and eventually moves to the right. What's more, the mode occurs at the highest frequency of the distribution that is on the left side of the median. Therefore, fashion <median <media.
In the box plot above, you can see that Q2 is present closer to Q1. This represents a positively skewed distribution. In terms of quartiles, can be given by:
In this case, it was very easy to know if the data is biased or not. But, What if we have something like this?
Here, Q2-Q1 and Q3-Q2 are equal and, but nevertheless, the distribution is positively skewed. The most attentive ones will have noticed that the length of the right mustache is greater than the left. From this, we can conclude that the data is positively biased.
Then, the first step is always to check the equality of Q2-Q1 and Q3-Q2. If it is the same, we look for the length of the whiskers.
Understanding the negatively skewed distribution
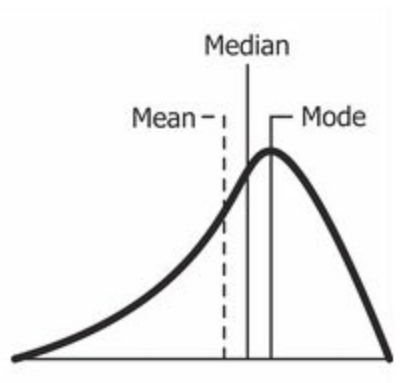
Source: Wikipedia
As you may have already guessed, a negatively skewed distribution is the distribution with the tail on its left side. The skewness value for a negatively skewed distribution is less than zero. You can also see from the figure above that the media <median <fashion.
In the box plot, the relationship between the quartiles for a negative skew is given by:
Similar to what we did before, if Q3-Q2 and Q2-Q1 are equal, then we look for the length of the whiskers. And if the length of the left mustache is greater than that of the right, then we can say that the data is negatively biased.
How do we transform skewed data?
Since you know how much skewed data can affect the prediction capabilities of our machine learning model, it is better to transform skewed data into normally distributed data. Here are some of the ways you can transform your skewed data:
- Power transformation
- Record transformation
- Exponential transformation
Note: The selection of the transformation depends on the statistical characteristics of the data.
Final notes
In this article, we cover the concept of asymmetry, its types and why it is important in the field of data science. We talk about asymmetry at the conceptual level, but if you want to go deeper, you can explore its math part as a next step.
What's more, You can read articles on other important statistical topics:
Connect with me in the comment section below if you have any questions.