This article was published as part of the Data Science Blogathon
Casi todo o todo tipo de información disponible en línea se almacena en algún tipo de databaseA database is an organized set of information that allows you to store, Manage and retrieve data efficiently. Used in various applications, from enterprise systems to online platforms, Databases can be relational or non-relational. Proper design is critical to optimizing performance and ensuring information integrity, thus facilitating informed decision-making in different contexts..... The amount of data and information online is quite large. Your Facebook profile picture, tus tweets, your previous food orders on Zomato: everything is stored somewhere.
Then, the question arises, Where are all these stored? The answer is simple.
A data base

(Image: https://www.pexels.com/photo/close-up-view-of-system-hacking-in-a-monitor-5380664/)
What is a database?
A database is a collection of related information. Modern databases contain millions or even trillions of pieces of information. Databases provide convenience for easy data storage and access.
The word 'datum’ means a single piece of information. The word data is the plural form of datum. One of the most important aspects of a database is to easily manage and operate large amounts of data..
Modern databases are managed by something called a Database Management System..
What is a database management system?
A database management system is software that helps users create and maintain a database. Database management systems manage large amounts of information, manage security, take care of data backups, import or export data and allow users to access the data.
What is a relational data base?
A database that follows the relational model and stores data in a tabular format is known as a relational database.. The database has rows and columns and a unique key for each data point.
Relational databases are very common and widely used. Almost everything you have entered online in a form or something like that is usually stored in a relational database. Examples of relational databases: Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, MYSQL.
Let's create a simple relational database using SQL.
SQL commands are written as follows.
CREATE TABLE student_data(
studentID int PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
student_name varchar(30),
gender VARCHAR(1),
course varchar(15),
marks float,
fees int,
admission_year int
);
A simple table consisting of sample data will be created. To give a brief information about the table created, the student is the PRIMARY KEY. As usual, this will be a student's registration number at a university or school. No puede ser NULLThe term "NULL" It is used in programming and databases to represent a null or non-existent value. Its main function is to indicate that a variable does not have a value assigned to it or that a piece of data is not available. And SQL, for instance, Used to manage records that lack information in certain columns. Understanding the use of "NULL" It is essential to avoid errors in data manipulation and..., namely, this field must have a value. The key word “NOT NULL” is used to define this.
Other columns of data include the student's name, the gender, the course, The qualifications, fees and year of admission.
A simple table consisting of sample data will be created. To give a brief information about the table created, the studentID is the MAIN KEY. As usual, this will be a student's registration number at a university or school. It cannot be NULL, namely, this field must have a value. The key word “NOT NULL” is used to define this.
Other columns of data include the student's name, the gender, the course, The qualifications, fees and year of admission.
Now, let's enter data in the table.
INSERT INTO student_data VALUES ('1', 'Rahul','M', 'BA English', 89.2, 15000, 2019);
INSERT INTO student_data VALUES ('2', 'Riya', 'F','BA History', 68, 12000, 2018);
INSERT INTO student_data VALUES ('3', 'Sagnik','M', 'MBBS', 96, 19000, 2019);
INSERT INTO student_data VALUES ('4', 'Aditya', 'M','BA English', 95, 8000, 2018);
INSERT INTO student_data VALUES ('5', 'Sunny', 'M','Btech', 78, 14000, 2019);
INSERT INTO student_data VALUES ('6', 'Anshuman', 'M','Btech', 67, 6000, 2018);
INSERT INTO student_data VALUES ('7', 'Soumya','M', 'Btech', 86.8, 17000, 2019);
INSERT INTO student_data VALUES ('8', 'Ravi', 'M','MBBS', 87.9, 18000, 2018);
INSERT INTO student_data VALUES ('9', 'Priya', 'F','BA English', 93, 12000, 2019);
INSERT INTO student_data VALUES ('10', 'Ankita', 'F','BA History', 89.2, 14000, 2018);
We insert 10 table entries.
The table now looks like this.
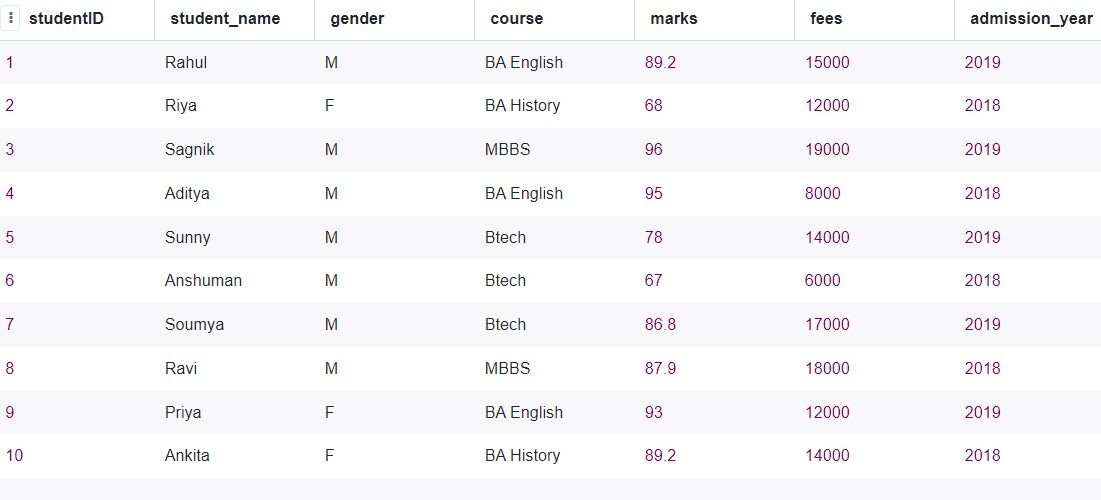
If you have found Excel, now you will understand that the visualization looks like Excel. For instance, each sheet contains some data in an excel file, each table contains some kind of information.
A table is a collection of related data entries and uses columns and rows to store data.
Each column is a data attribute, in the table above, gender, course, trademarks, etc. are the data fields or attributes. The rows are called records, are the individual table entries.
This way of storing data is easy, flexible and efficient. New entries can simply be added to the end of the table. Computer scientist Edgar F. Codd developed the relational model of data storage in 1970.
How do relational databases work?
All the parts mentioned above are important aspects of relational databases. To sum up, The tables, known as relationships, consist of data in rows and columns. Todas las tablas tienen una Primary KeyThe primary key is a fundamental concept in databases, used to uniquely identify each record within a table. It consists of one or more attributes that cannot contain null values and must be unique. Its correct design is crucial to maintain data integrity, facilitating relationships between tables and optimizing queries. Without a primary key, ambiguities and errors could be generated in the.... The logical connection between two or more tables can be established with the help of foreign keys. A foreign key is a column that refers to the primary key of another table.
Relationships between multiple tables can be defined or modeled using an entity relationship diagram. Has all entities and attributes. In RDBM, a measureThe "measure" it is a fundamental concept in various disciplines, which refers to the process of quantifying characteristics or magnitudes of objects, phenomena or situations. In mathematics, Used to determine lengths, Areas and volumes, while in social sciences it can refer to the evaluation of qualitative and quantitative variables. Measurement accuracy is crucial to obtain reliable and valid results in any research or practical application.... que los datos se almacenan en formato de tabla, relationships are also stored in table format.
Relational databases are the most used, support data independence and data stored as tables can be easily analyzed and processed.
For instance, consider the data of previous students. Here, there is 10 tickets, but suppose a real life situation and there is 5000 students. We cannot analyze each data point individually.
Let's say we have to see the distribution of the grades, count the number of male and female students and perform other data exploration tasks. RDBMS will facilitate these things.
What to do is quite simple. Data can be extracted, convert to excel file and analyze in excel. Or it can be converted to a csv file and parsed in Excel. After that, it is quite easy to work with the data.
RDBM relational model helps separate logical data structures from physical storage structures. This allows database administrators to manage the storage of physical data without affecting access to that data as a logical structure..
Relational databases provide a way to store and represent data, that can be used by any application or software. The main strength of relational databases is the use of tables to store data. Tables are a simple way, robust and flexible data storage.
SQL has become the most popular language for database queries. SQL can easily be used to retrieve data from databases. Let's implement some simple SQL queries.
SQL queries:
Now, from the previously created student database, Let's say, we want to get all the grades of the students, sorted in ascending order. The SQL query will be:
SELECT student_data.student_name, student_data.marks FROM student_data ORDER BY marks;
Production:
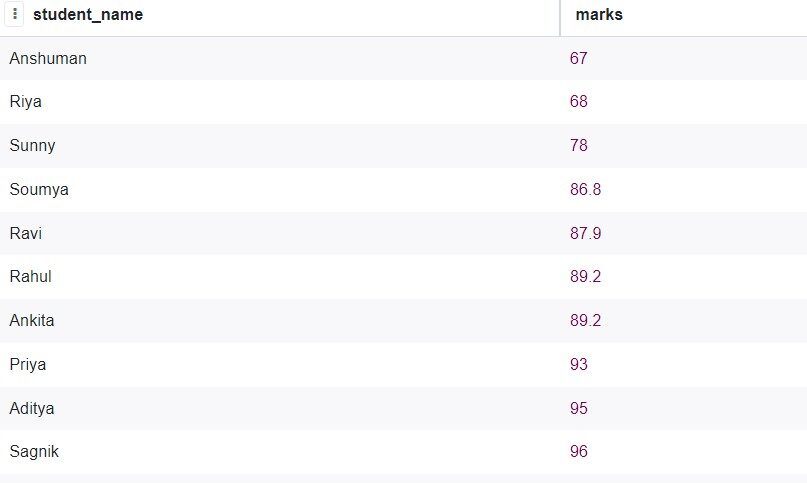
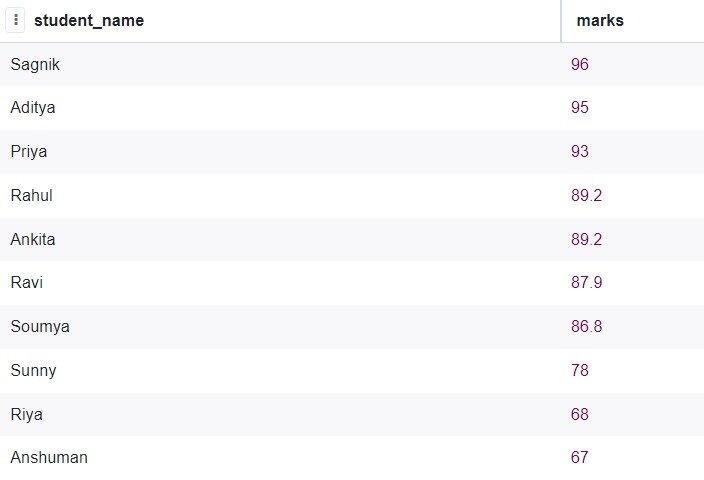
Now, we want the same result, but in descending order.
The SQL query will be:
SELECT student_data.student_name, student_data.marks FROM student_data ORDER BY marks DESC;
Production:
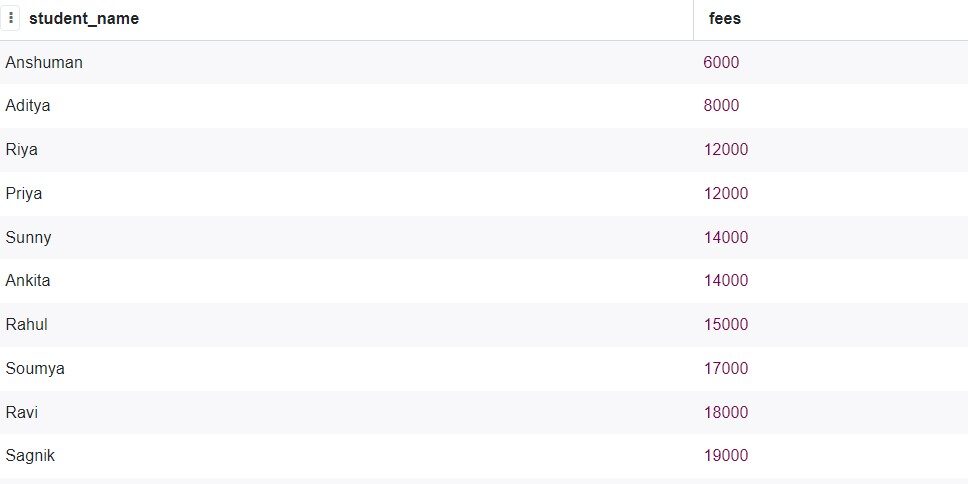
Now, we want to analyze student fees, let's see how to implement them.
The SQL query is quite simple.
SELECT student_name, fees FROM student_data ORDER BY fees;
Production:
Now, let's take the students who are in the BTech course.
The query is as follows.
SELECT student_name, course,fees, marks FROM student_data WHERE course= "Btech";
Production:
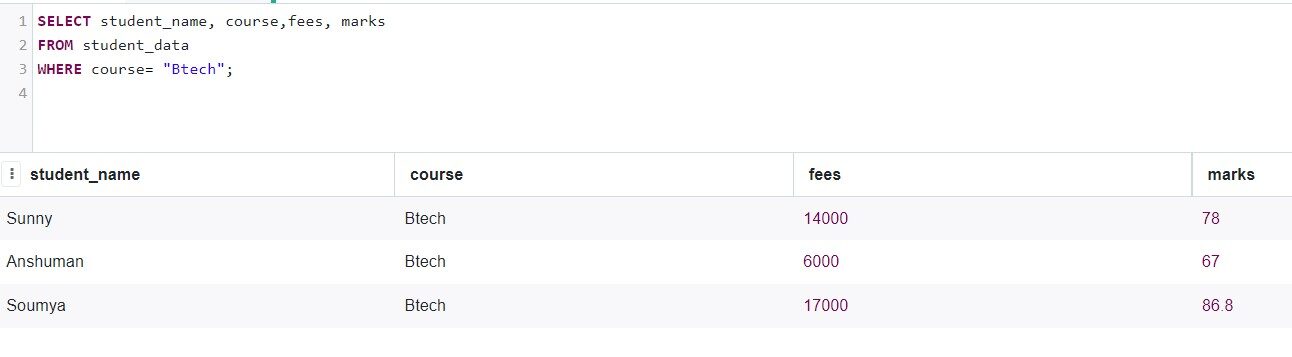
The online SQL tool used is: https://sqliteonline.com/
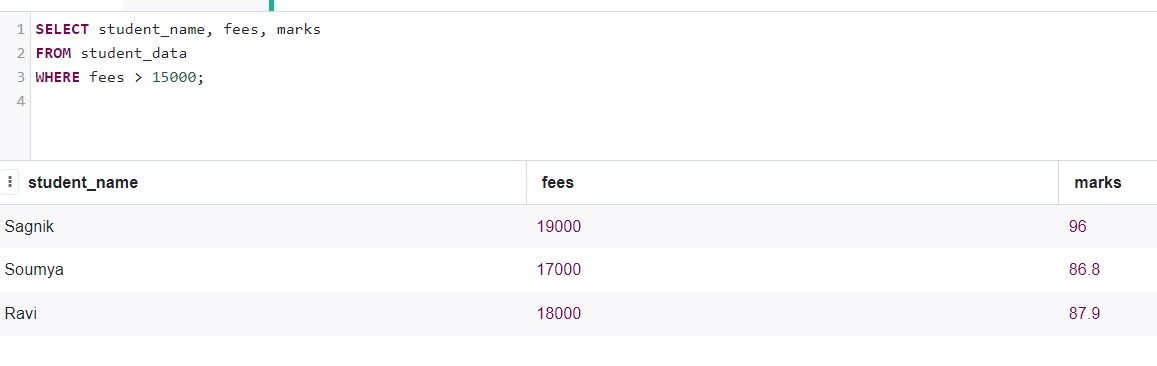
Now, Let's check which students have fees higher than 15000.
SELECT student_name, fees, marks FROM student_data WHERE fees > 15000;
Production:
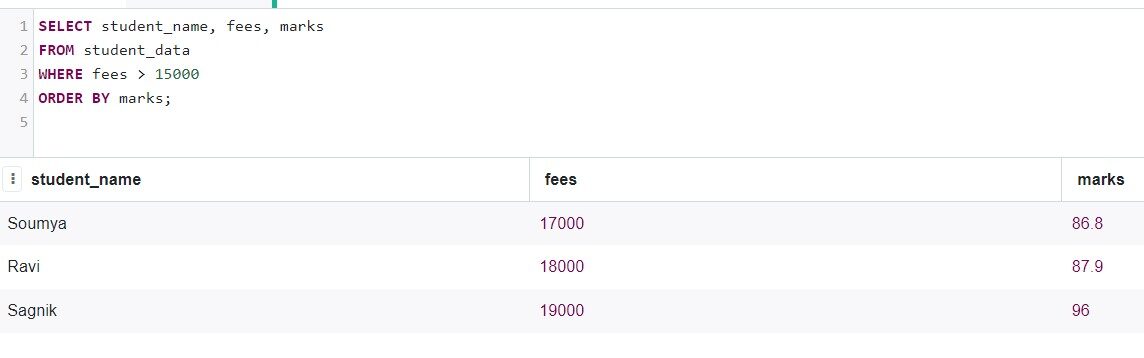
Now, Let's review students whose fees are higher than 15000, and the entries are sorted by their grades.
SELECT student_name, fees, marks FROM student_data WHERE fees > 15000 ORDER BY marks;
Production:
Now, Let's choose students who have taken a Bachelor's degree in English or MBBS, then we will sort them by the rates.
SELECT student_name, fees, marks, course
FROM student_data
WHERE course in('BA English','MBBS')
ORDER BY fees;
Production:
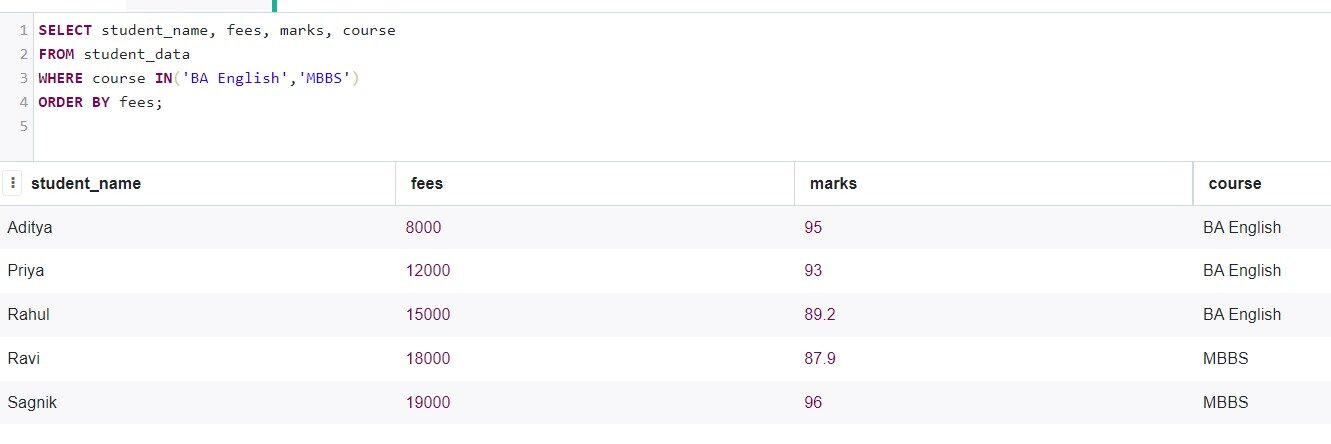
Then, we can see that getting and retrieving data from a relational database is very easy.
The tabular structure of relational databases is the main advantage of such databases. These databases are also very simple and queries can be used to extract data or modify existing data. The stored data is also very accurate. Data validity checks and data typing ensure data integrity. By allowing access to specific people, RDBMs also take care of the security issue.
Relational databases have a well-defined relationship between tables. Tables are related to each other, making data search easy and reporting data easy and simple. Relational databases are very important, since they have created a universal model to store information and data. Most modern computers can use relational databases.
People understand them well, scaling and expansion are easy, and they also fit the use case most of the time. That is why relational databases are mainly used.
About me:
Prateek Majumder
AnalyticsAnalytics refers to the process of collecting, Measure and analyze data to gain valuable insights that facilitate decision-making. In various fields, like business, Health and sport, Analytics Can Identify Patterns and Trends, Optimize processes and improve results. The use of advanced tools and statistical techniques is essential to transform data into applicable and strategic knowledge.... | Content creation
Connect with me on Linkedin.
My other articles on DataPeaker: Link.
Thanks.
The media shown in this article is not the property of DataPeaker and is used at the author's discretion.






